Introduction
The Comparison between Different AWS Services is a Series containing different blog posts that provide a basic understanding of key differences Between different aws services. Each post covers the detailed guide on difference between the AWS Services and Which is preferred more . This series aims at providing "Comparison Between Different AWS Services."
The storage strategy you choose plays a major role in the performance you receive, as well as the costs you’ll expend. To achieve peak efficiency, you must match your computing, application, and processing needs to the appropriate storage technology. But which option is right for you?
To answer this question, we’ll explore the differences between Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS), Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS), and Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and understand each solution’s unique benefits and uses. This will make it easier to pick the best solution to support your business objectives and storage needs.
My Background: I am Cloud , DevOps & Big Data Enthusiast | 4x AWS Certified | 3x OCI Certified | 3x Azure Certified .
What’s The Difference Between Amazon EBS Vs EFS Vs S3?
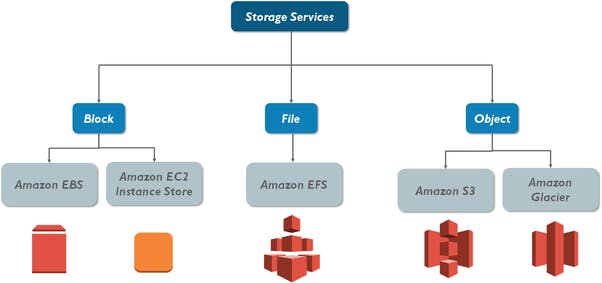
Amazon EFS, Amazon EBS, and Amazon S3 are AWS’ three different storage types that can be applicable for different types of workload needs. Let’s take a closer look at the key features of each option, as well as the similarities and differences.
Amazon EBS delivers high-availability block-level storage volumes for Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances. It stores data on a file system which is retained after the EC2 instance is shut down. Amazon EFS offers scalable file storage, also optimized for EC2. It can be used as a common data source for any application or workload that runs on numerous instances. Using an EFS file system, you may configure instances to mount the file system. The main differences between EBS and EFS is that EBS is only accessible from a single EC2 instance in your particular AWS region, while EFS allows you to mount the file system across multiple regions and instances.
Finally, Amazon S3 is an object store good at storing vast numbers of backups or user files. Unlike EBS or EFS, S3 is not limited to EC2. Files stored within an S3 bucket can be accessed programmatically or directly from services such as AWS CloudFront. This is why many websites use it to hold their content and media files, which may be served efficiently from AWS CloudFront.
So how can you choose between Amazon EBS vs EFS vs S3?
That depends on what benefits you’re looking for, and your use case for your workload. Let’s take an in-depth look at each one to understand their benefits and use cases.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
Use Amazon EBS to provide storage for the drives of your virtual machines. It stores data in equally-sized blocks and organizes them into a hierarchy similar to a traditional file system. The volumes are provisioned in size and attached to EC2 instances in a way that’s similar to the local disk drive on a physical machine. Here are EBS’ benefits and use cases:
Amazon EBS Benefits
Performance optimization: Increase throughput by devoting network capacity and minimizing the network contention between your instances and EBS.
Low-latency performance: By using SSD EBS volumes, it offers reliable I/O performance scaled to meet your workload needs. Highly available and secure storage: EBS volumes offer redundancy within its Availability Zones while access control and encryption bolster security.
Geographic interchangeability: With EBS, you can duplicate snapshots throughout AWS regions and place resources and data in multiple locations. This makes disaster recovery, data center migration, and geographical expansion simple.
Easy data backup and restoration: Point-in-time volume snapshots safeguard data.
Rapid up- or down-scaling: EBS can quickly scale volumes, ensuring you get the right performance and capacity for changing computing needs.
Amazon EBS Use Cases
Testing and development: You can scale, archive, duplicate or provision your testing, development, or production environments.
NoSQL databases: EBS offers NoSQL databases the low-latency performance and dependability they need for peak performance. Relational databases: EBS scales to meet your changing storage needs. This makes it a great choice for deploying databases, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, or Microsoft SQL Server.
Business consistency: Copy EBS Snapshots and Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) to run applications in different AWS regions. This reduces data loss and speeds recovery time by backing up log files and data regularly, across geographies.
Enterprise-wide applications: It can meet a variety of enterprise computing needs through powerful block storage that can support your most important applications, such as Microsoft Exchange, Oracle, or Microsoft SharePoint.
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS)
EFS is the best choice for running any application that has a high workload, requires scalable storage, and must produce output quickly. It scales automatically, even to meet the most abrupt workload spikes. After the period of high-volume storage demand has passed, EFS will automatically scale back down. EFS can be mounted to different AWS services and accessed from all your virtual machines. Use it for running shared volumes, or for big data analysis. You’ll always pay for the storage you actually use, rather than provisioning storage in advance that’s ultimately wasted.
Amazon EFS Benefits
Performance that scales to support any workload: EFS offers the throughput changing workloads need. It can provide higher throughput in spurts that match sudden file system growth, even for workloads up to 500,000 IOPS or 10 GB per second.
Energetic elasticity: Automatically scale your file system storage up or down. Remove or add files and never disturb applications. Once you make your EFS file system you can add files without worrying about storage provisioning.
Accessible file storage: On-premises servers and EC2 instances can access shared file systems concurrently. EC2 instances can also access EFS file systems located in other AWS regions through VPC peering.
Comprehensive managed service: EFS is a complete managed service, meaning your firm will never have to patch, deploy, or maintain your file system.
Cost savings: The only storage you’ll pay for is exactly what you use, as there’s no advance provisioning, up-front fees, or commitments. Moreover, you can use Lifecycle Management to transfer files that have been unused for a month to a more cost-effective storage class, which can lower expenses up to 85%. Tighter security and compliance: You can securely access the file system with your current security solution, or control access to EFS file systems using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), or POSIX permissions. And, EFS can encrypt your data, whether it’s in transit or at rest. This gives you dependable security and makes regulatory compliance easier.
Amazon EFS Use Cases
Lift-and-shift application support: EFS is elastic, available, and scalable, and enables you to move enterprise applications easily and quickly without needing to re-architect them.
Analytics for big data: It has the ability to run big data applications, which demand significant node throughput, low-latency file access, and read-after-write operations.
Content management system and web server support: EFS is a robust throughput file system capable of enabling content management systems and web serving applications, such as archives, websites, or blogs.
Application development and testing: Only EFS provides a shared file system needed to share code and files, across multiple compute resources to facilitate auto-scaling workloads.
Amazon S3
Amazon S3 provides object storage. Each object has its own unique identifier or key, for access through web requests from any location. S3 also supports static web content hosting that can be accessed from the S3 bucket or from AWS CloudFront. And S3 is notably secure, providing. “eleven nines” - 99.999999999 of data durability.
Amazon S3 Benefits
Robust performance, scalability, and availability: Amazon S3 scales storage resources free from resource procurement cycles or investments upfront. It keeps your data safe from errors, failures, and threats and makes it available when you need it. Cost-saving storage classes: Storing data throughout S3 storage classes saves costs and maintains high levels of performance. Storage class analysis enables you to locate data that may be moved to a lower-cost storage class. Then you can make the transfer using an S3 Lifecycle policy.
Finally, S3 intelligent-tiering enables the storage of data that has changing or unknown access patterns by tiering objects, which cuts storage costs.
Easier security, compliance, and audit features: S3 can store data and protect it from unauthorized access using its powerful access management and encryption tools. S3 has features that make it easy to comply with regulatory requirements, and Amazon Macie can deny irregular access requests to your sensitive data. Plus, S3 works well with AWS’ many auditing features.
Exacting data control: An array of management tools enable you to classify and report on data. S3 has storage class analysis that monitors access patterns, while S3 Lifecycle analyzes object transfers to lower-cost storage. S3 Object Lock assigns retention dates to objects to prevent deletion, and S3 Inventory offers visibility of stored objects and their encryption and metadata. Finally, S3 Batch Operations can run storage management maintenance for billions of objects while AWS Lambda can be used to automate workflows, define alerts and log activities without added management of infrastructure.
Amazon S3 Use Cases
Data lake and big data analytics: Create a data lake to hold raw data in its native format, then use machine learning tools, query-in-place, and analytics to draw insights. S3 works with AWS Lake Formation to create data lakes, then define governance, security, and auditing policies. Together, they can be scaled to meet your growing data stores, and you’ll never have to make an investment upfront.
Backup and restoration: Secure, robust backup and restoration solutions are easy to build when you combine S3 with other AWS offerings, including EBS, EFS, or S3 Glacier. These offerings enhance your on-premises capabilities, while other offerings can help you meet compliance, recovery time, and recovery point objectives.
Reliable disaster recovery: S3 storage, S3 Cross-Region Replication and additional AWS networking, computing, and database services make it easy to protect critical applications, data, and IT systems. It offers nimble recovery from outages, no matter if they are caused by system failures, natural disasters, or human error.
Methodical archiving: S3 works seamlessly with other AWS offerings to provide methodical archiving capabilities. S3 Glacier and S3 Glacier Deep Archive enable you to archive data and retire physical infrastructure. There are three S3 storage classes you can use to retain objects for extended periods of time at their lowest rates.
S3 Lifecycle policies can be created to archive objects at any point within their lifecycle, or you can upload objects to archival storage classes directly.
S3 Object Lock meets compliance regulations by applying retention dates objects to avoid their deletion. And unlike a tape library, S3 Glacier can restore any archived object within minutes.
Hope this guide helps you understand the Different AWS Storage Options, feel free to connect with me on LinkedIn. You can view my badges here. If you are interested in learning more about AWS then follow me on github. If you liked this content then do clap and share it . Thank You .
